Super Charger VS Turbo Charger
Last updated on – Feb 28, 2016
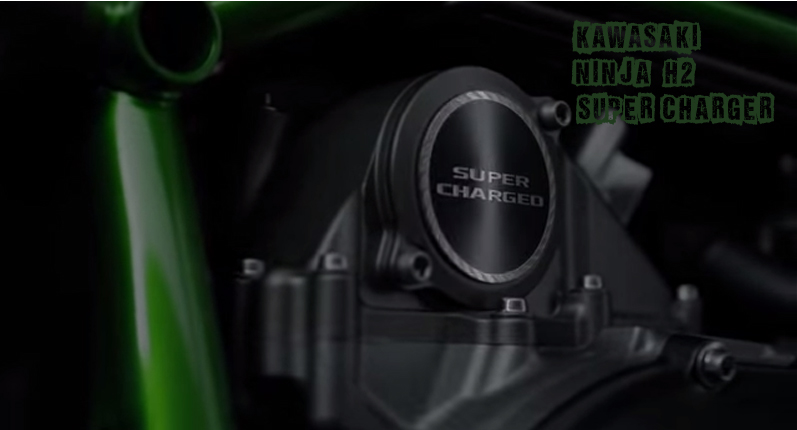
The Kawasaki Ninja H2 is now about a week old thing, which will remain new in the category of superbikes with Forced Induction Systems. The street version of the same is also about to reach the shores in the upcoming EICMA and AIMExpo events. Though, these systems were subject to the car’s power enhancement in earlier days, but it has become a myth now as the motorbikes have also started employing them for enjoying the rides. It is the dawn of this technology in two wheelers which might become a great thing in the future…… with some difficulties to Cherish.
Now, at this point of life, you would be seeking the relevance of the title of this article. The terms used here are the types of Forced Induction Systems. The basic function and operation will make you decide a better companion for your machine.
FORCED INDUCTION SYSTEM
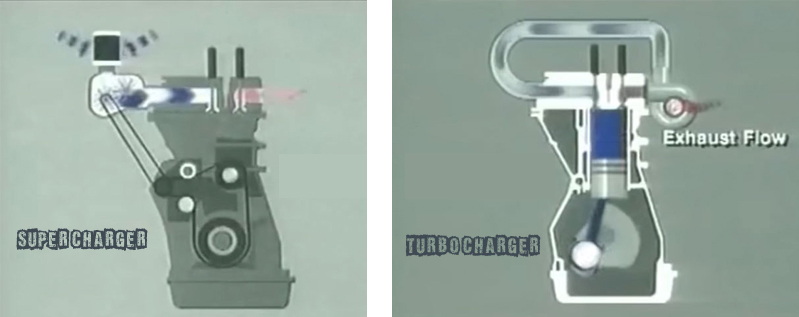
Forced Induction Systems are used to boost the flow of air into the engine. The air always gets into the bike’s engine via carburetor or fuel injection while getting mixed with the fuel in a proper ratio. To boost this flow of air into the engine, we require an apparatus to be connected externally. The superchargers and turbochargers are the furnishings, which play the role of doing this job. The role and functioning of both these FIS are quite similar, yet they possess differences to hold the dignity of their application.
The major fields of application of these FIS can be found in hilly terrains and race tracks. Though, as I mentioned above that the engine requires the mixture of air and fuel, the absorption of air from the atmosphere varies with the amount of oxygen getting collided with the radiator and/or other fuel supply systems. An engine starts experiencing trouble while climbing up and at places which are at a good height from the sea level. The reason behind this is the lack of oxygen. Scientifically, at sea level, the amount of usable oxygen is 0.016lbs per cubic foot, which gradually decreases upto 0.010lbs per cubic foot on anchoring 15,000 feet of height from sea level. The drop in volume of air effects the power and efficiency of the engine badly and ending the journey in stress. At the moment of route, one would think of raising the caliber of their engine for which technologies have created two master players.
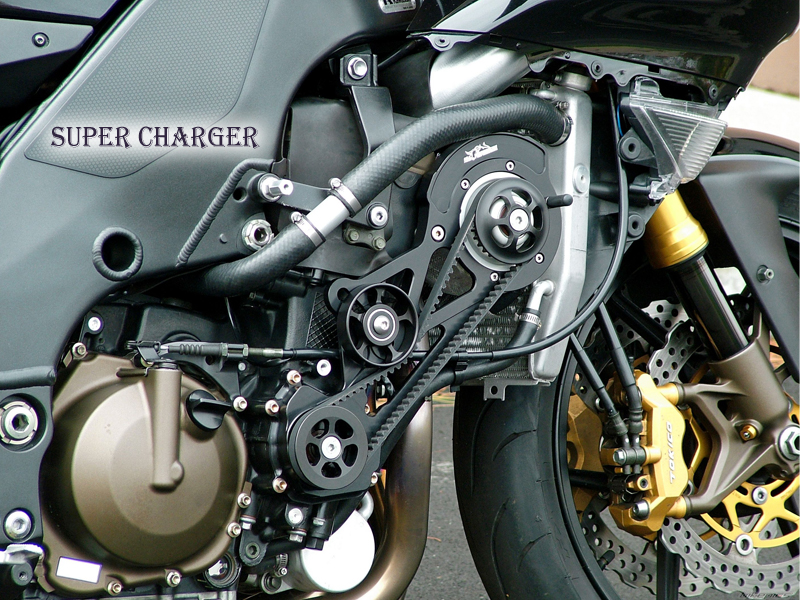
SUPER CHARGER
SuperCharger is a forced induction system which assembles at the inlet port of the engine. The SuperChargers are composed of compressor units which exerts the air at a commendable pace. Now, the Compressor inside the FIS doesn’t rotate automatically, it requires some powering gizmo for action. Hence, it is also been stuffed with a mechanism to connect it to the engine’s crank via belt or chain. As the rider stretches the throttle, the crank gets into the motion with the RPM corresponding to the throttle response. With the raising speed, more air gets inserted into the engine, eventually turning it into a highly capable mechanical monster.
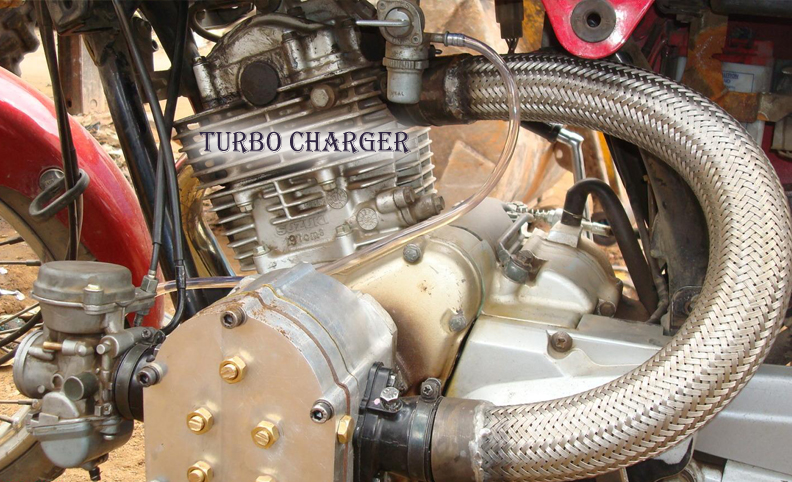
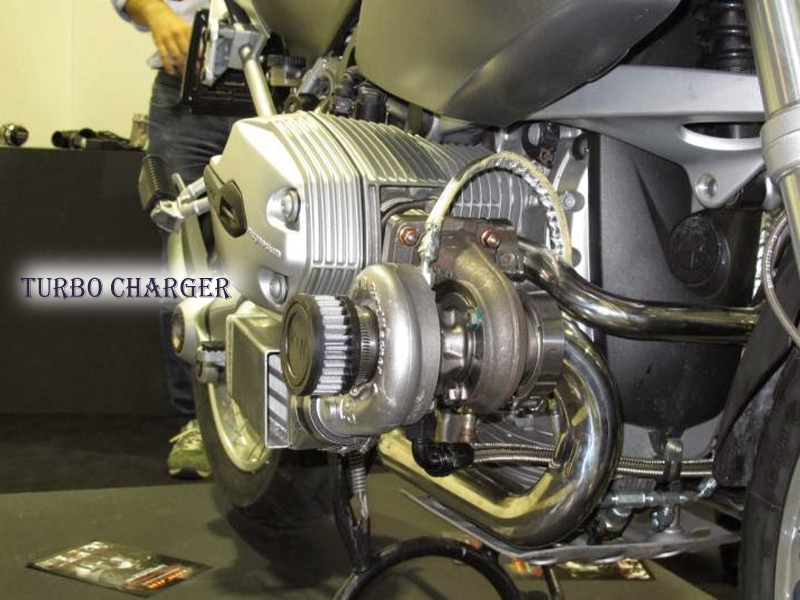
TURBO CHARGER
TurboChargers works for the same motto over which super chargers work, but the way of executing the same task is different. The equipment is piled up at the exhaust point of the engine. This apparatus is composed of turbine for the accomplishment of the process. The smoke from the engine revolves the turbine, which stretches air from the atmosphere. To transfer this air into the engine, a hose is connected to the inlet of the engine. In simple words, the bad gas from the engine helps the rider to get more power out of their machine. Rolling further, it is better in efficiency than the superchargers with certain pros over the same.
An FIS engaged engine can generate more power than a regular engine and the hike in power depends upon the amount of air intake. Usually, the engines with chargers pull 50% more air. Hence, they are supposed to replicate it over the performance as well, but practically one can get around 35% to 40% of raised power.
Both Have the Same Action, then What’s the Big Deal?
With the above discussion, we can summarize that the Superchargers and Turbochargers have almost same functions and processing, then what distinguishes them apart? Since the Superchargers are set into force by connecting it with the engine’s crankshaft, the rider needs to stretch the throttle harder to get the ultimate power. This means, we require power for the generation of power. Additionally, the compressor will reduce the function on loosening the throttle. It doesn’t sound as a favourable business as a good lot of energy is being wasted. For example, if an engine can generate 400BHP of power from 240BHP on applying supercharger, then it will generate only 340BHP with wastage of about 13% to 15%. This calculation is not standard or authentic and may vary with the engine and other configurations.
On the other Hand, TurboChargers uses exhausted smoke to rotate the turbine. More smoke will make it rotate more powerfully and hence more power will be drilled out of the cylinders. The smoke production is a constant process and it keeps the turbine moving at all times. Thus, it makes the system economic and doesn’t place burden over the crank, but TurboChargers starts delivering power after a short interval from the juncture of engine’s start up.
Why SuperCharger?
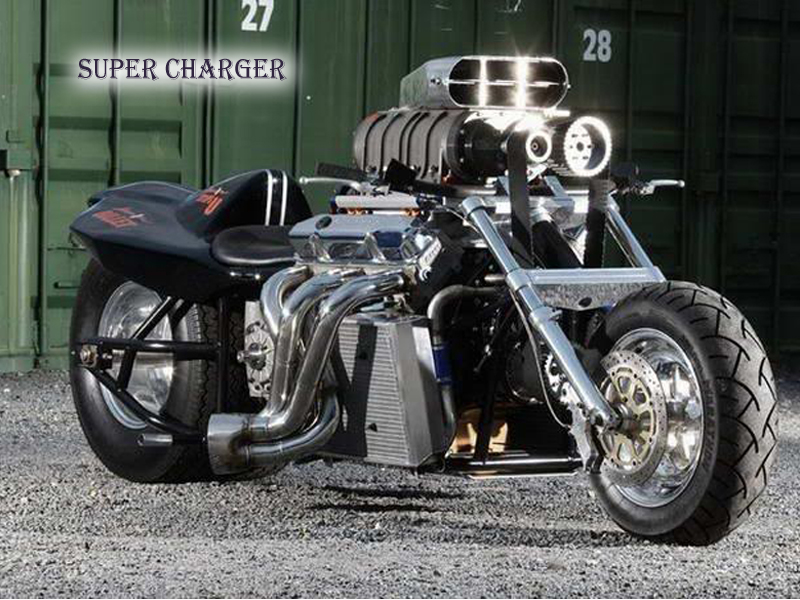

To count the Advantages of SuperCharger over TurboCharger, refer to the following points
- The power will start getting boosted from the moment when the engine starts thumping.
- The turbo lag doesn’t occur in SuperCharged engines.
Why TurboCharger?
The TurboCharger over the SuperCharger is a much practical choice because of following points
- The Apparatus being attached to exhaust doesn’t stretch power from engine, making it economical.
- The engine will work comfortably as no external stuff will disturb it.
Super Charger VS Turbo Charger
https://www.blog.sagmart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/super-and-turbo-chargers-300x300.jpg AutomobilesBikes Reviews and TipsLast updated on – Feb 28, 2016
The Kawasaki Ninja H2 is now about a week old thing, which will remain new in the category of superbikes with Forced Induction Systems. The street version of the same is also about to reach the shores in the upcoming EICMA and AIMExpo events. Though, these systems were subject to the car’s power enhancement in earlier days, but it has become a myth now as the motorbikes have also started employing them for enjoying the rides. It is the dawn of this technology in two wheelers which might become a great thing in the future…… with some difficulties to Cherish.
Now, at this point of life, you would be seeking the relevance of the title of this article. The terms used here are the types of Forced Induction Systems. The basic function and operation will make you decide a better companion for your machine.
FORCED INDUCTION SYSTEM
Forced Induction Systems are used to boost the flow of air into the engine. The air always gets into the bike’s engine via carburetor or fuel injection while getting mixed with the fuel in a proper ratio. To boost this flow of air into the engine, we require an apparatus to be connected externally. The superchargers and turbochargers are the furnishings, which play the role of doing this job. The role and functioning of both these FIS are quite similar, yet they possess differences to hold the dignity of their application.
The major fields of application of these FIS can be found in hilly terrains and race tracks. Though, as I mentioned above that the engine requires the mixture of air and fuel, the absorption of air from the atmosphere varies with the amount of oxygen getting collided with the radiator and/or other fuel supply systems. An engine starts experiencing trouble while climbing up and at places which are at a good height from the sea level. The reason behind this is the lack of oxygen. Scientifically, at sea level, the amount of usable oxygen is 0.016lbs per cubic foot, which gradually decreases upto 0.010lbs per cubic foot on anchoring 15,000 feet of height from sea level. The drop in volume of air effects the power and efficiency of the engine badly and ending the journey in stress. At the moment of route, one would think of raising the caliber of their engine for which technologies have created two master players.
SUPER CHARGER
SuperCharger is a forced induction system which assembles at the inlet port of the engine. The SuperChargers are composed of compressor units which exerts the air at a commendable pace. Now, the Compressor inside the FIS doesn’t rotate automatically, it requires some powering gizmo for action. Hence, it is also been stuffed with a mechanism to connect it to the engine’s crank via belt or chain. As the rider stretches the throttle, the crank gets into the motion with the RPM corresponding to the throttle response. With the raising speed, more air gets inserted into the engine, eventually turning it into a highly capable mechanical monster.
TURBO CHARGER
TurboChargers works for the same motto over which super chargers work, but the way of executing the same task is different. The equipment is piled up at the exhaust point of the engine. This apparatus is composed of turbine for the accomplishment of the process. The smoke from the engine revolves the turbine, which stretches air from the atmosphere. To transfer this air into the engine, a hose is connected to the inlet of the engine. In simple words, the bad gas from the engine helps the rider to get more power out of their machine. Rolling further, it is better in efficiency than the superchargers with certain pros over the same.
An FIS engaged engine can generate more power than a regular engine and the hike in power depends upon the amount of air intake. Usually, the engines with chargers pull 50% more air. Hence, they are supposed to replicate it over the performance as well, but practically one can get around 35% to 40% of raised power.
Both Have the Same Action, then What’s the Big Deal?
With the above discussion, we can summarize that the Superchargers and Turbochargers have almost same functions and processing, then what distinguishes them apart? Since the Superchargers are set into force by connecting it with the engine’s crankshaft, the rider needs to stretch the throttle harder to get the ultimate power. This means, we require power for the generation of power. Additionally, the compressor will reduce the function on loosening the throttle. It doesn’t sound as a favourable business as a good lot of energy is being wasted. For example, if an engine can generate 400BHP of power from 240BHP on applying supercharger, then it will generate only 340BHP with wastage of about 13% to 15%. This calculation is not standard or authentic and may vary with the engine and other configurations.
On the other Hand, TurboChargers uses exhausted smoke to rotate the turbine. More smoke will make it rotate more powerfully and hence more power will be drilled out of the cylinders. The smoke production is a constant process and it keeps the turbine moving at all times. Thus, it makes the system economic and doesn’t place burden over the crank, but TurboChargers starts delivering power after a short interval from the juncture of engine’s start up.
Why SuperCharger?

To count the Advantages of SuperCharger over TurboCharger, refer to the following points
- The power will start getting boosted from the moment when the engine starts thumping.
- The turbo lag doesn’t occur in SuperCharged engines.
Why TurboCharger?
The TurboCharger over the SuperCharger is a much practical choice because of following points
- The Apparatus being attached to exhaust doesn’t stretch power from engine, making it economical.
- The engine will work comfortably as no external stuff will disturb it.



Leave a Reply